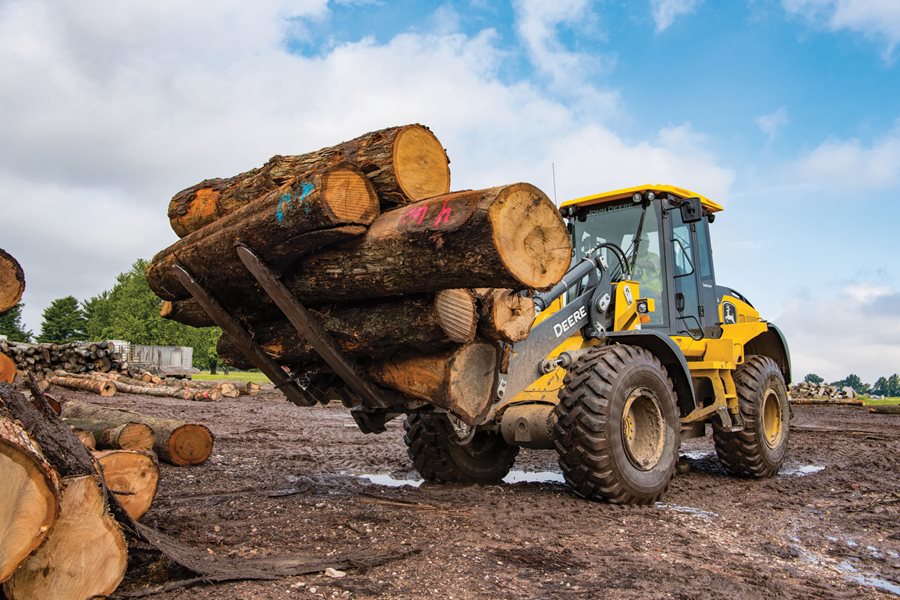
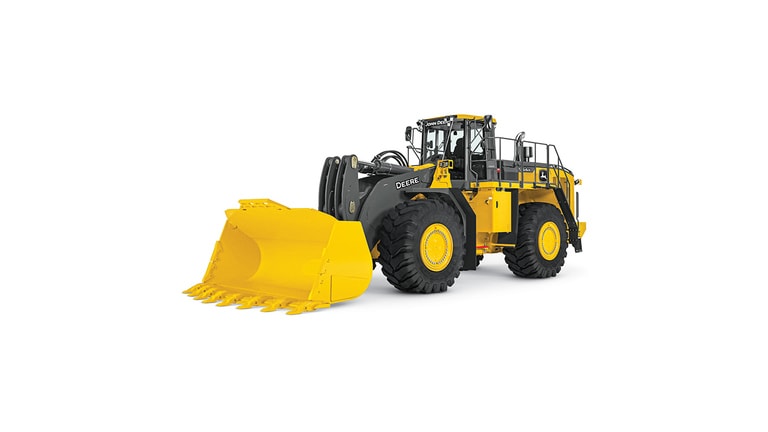
Wheel Loaders
When your material-handling application needs a heavy-duty lift, add a P-Tier Wheel Loader to your lineup. Combining convenient front-end features with near-parallel lift, spacious operator stations including customizable ergonomic electrohydraulic (EH) controls, and streamlined electrical and hydraulic routing, these versatile and productive mid-size models are designed to help you take your operation to the next level.
Request a QuoteExplore Wheel Loader Models
Pick Your Performance Tier
Different jobs call for different solutions. With John Deere Performance Tiering, you'll find the right equipment. Each tier offers distinct levels of performance, comfort, innovation, and serviceability, at a price to match. What doesn't change, regardless of your tier, is the quality and support you've come to rely on from Doggett.
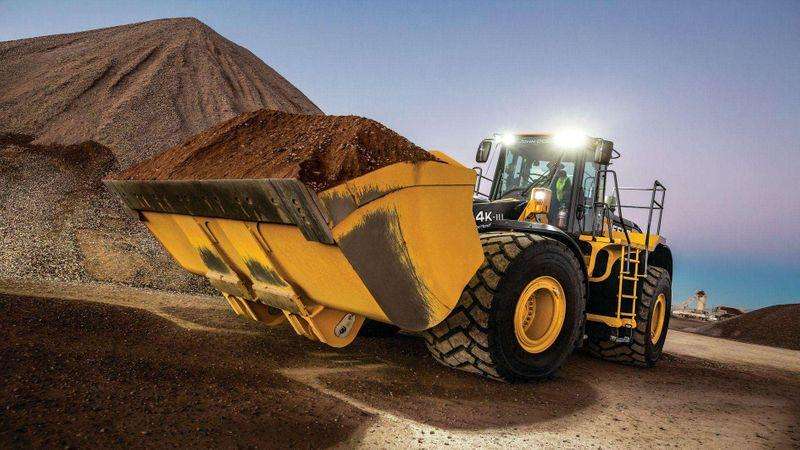

Payload Weighing
Payload weight is displayed on the monitor during loading, with real-time load and tonnage data transmitted via JDLink™, access to accurate payload values removes the guesswork from daily production levels, increasing uptime and efficiency.
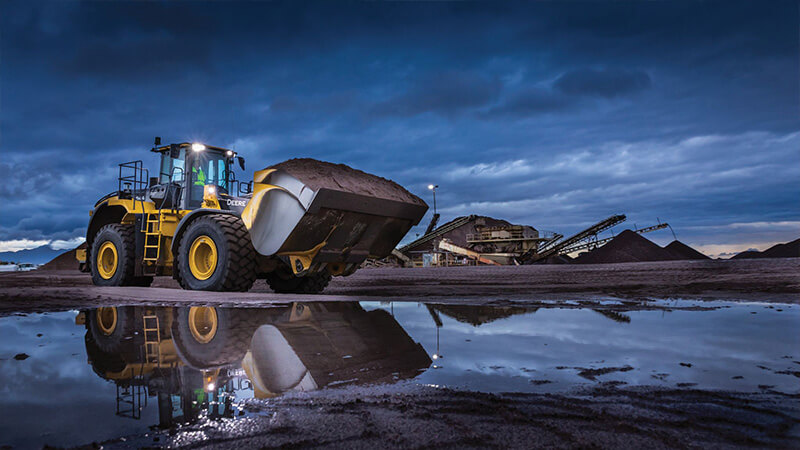

Remote Diagnostics and Support
To maximize uptime and lower costs, JDLink™ connectivity provides machine location, utilization data, and alerts to help you maximize productivity and efficiency. JDLink also enables John Deere Connected Support™.
Doggett John Deere uses Expert Alerts based on data from thousands of connected machines to proactively address conditions that may otherwise likely lead to downtime. We can also monitor machine health and leverage remote diagnostics and programming capability to further diagnose problems and even update machine software without a time-consuming trip to the jobsite.
Features and Specifications
Considering the features and specifications of a wheel loader before purchasing is essential, ensuring you select the suitable machine for your needs and maximizing your productivity and profitability.
Hydraulic Flow
The hydraulic flow refers to the amount of hydraulic fluid that can be transferred to the loader’s hydraulic system, which powers various functions, such as the loader arm and bucket. The hydraulic flow is typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM), and a higher flow rate allows for faster and more powerful hydraulic operations.
Load Capacity
The load capacity is the maximum weight of materials the loader can safely carry in its bucket. The load capacity of a wheel loader is influenced by several factors, including the machine’s size, the strength of its frame, and the lifting capacity of its hydraulic system.
Lift Height
The lift height of a wheel loader is the maximum height to which it can raise its bucket. The loader arms’ length, the loader boom’s size, and the hydraulic system’s lifting capacity determine the lift height. The lift height is an important factor to consider when working in areas with limited overhead clearance.

Linkage Configuration
The linkage configuration of a wheel loader refers to the mechanical linkage that connects the loader’s hydraulic system to its bucket or other attachments. There are two main types of linkage configurations: Z-bar and parallel. The Z-bar linkage provides high breakout force and good bucket roll-back, while the parallel link offers superior visibility and precise control of the bucket.

Rigid or Articulated
The choice between a rigid or articulated wheel loader depends on the specific application. Rigid wheel loaders have a fixed frame and are better suited for applications requiring high stability and power, such as mining and heavy construction. Articulated wheel loaders have a pivot point between the front and rear frames, allowing excellent maneuverability in tight spaces and better traction on uneven terrain.
FAQs about Construction Equipment Wheel Loaders
Can I purchase a John Deere wheel loader at a store?
Yes, you can. Find the John Deere wheel loader of your choice and click on it to go to the product page. Click on the “Find a dealer” button which will take you to our locations page. From there, you can see our various dealer locations in Texas and Louisiana. We provide addresses, phone numbers, and links to dealer pages.
What is the difference between a wheel loader and a bulldozer?
A wheel loader is often used for digging and transporting soil, while a bulldozer is used for flattening earth. Typically, a wheel loader is mounted on wheels (hence the name), while a bulldozer is mounted on tracks.
What type of steering is available for John Deere wheel loaders?
Each John Deere wheel loader comes with a joystick as the default controller. This helps with forward visibility. Steering wheel options are usually available for each of our wheel loaders.
Do you sell attachments for your wheel loaders?
Yes, we do. Browse through our attachments inventory to find the parts that you need. When looking for a wheel loader for sale, don’t forget to buy the attachments you need to get the most out of your wheel loader.
What’s the difference between the various tiers for wheel loaders?
These performance tiers were conceived to help customers find the best value for their budgets. Our X-tier machines represent the most advanced in features and tech. P-tier machines provide great value by yielding high output for the task at hand. G-tier machines are designed to be the most economical.



